Problem statement
You are given an m x n binary matrix mat of 1's (representing soldiers) and 0's (representing civilians). The soldiers are positioned in front of the civilians. That is, all the 1's will appear to the left of all the 0's in each row.
A row i is weaker than a row j if one of the following is true:
- The number of soldiers in row
iis less than the number of soldiers in rowj. - Both rows have the same number of soldiers and
i < j.
Return the indices of the k weakest rows in the matrix ordered from weakest to strongest.
Example 1
Input: mat =
[[1,1,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,0],
[1,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,1]],
k = 3
Output: [2,0,3]
Explanation:
The number of soldiers in each row is:
- Row 0: 2
- Row 1: 4
- Row 2: 1
- Row 3: 2
- Row 4: 5
The rows ordered from weakest to strongest are [2,0,3,1,4].
Example 2
Input: mat =
[[1,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,0,0,0],
[1,0,0,0]],
k = 2
Output: [0,2]
Explanation:
The number of soldiers in each row is:
- Row 0: 1
- Row 1: 4
- Row 2: 1
- Row 3: 1
The rows ordered from weakest to strongest are [0,2,3,1].
Constraints
m == mat.length.n == mat[i].length.2 <= n, m <= 100.1 <= k <= m.matrix[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution 1: Addition and Sorting
Compute the number of soldiers for each row and sort the rows based on the "weaker row" criteria.
Code 1
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int> kWeakestRows(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int k) {
using myPair = pair<int,int>;
vector<myPair> v;
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); i++) {
int num = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < mat[i].size(); j++) {
num += mat[i][j];
}
v.push_back(make_pair(i, num));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](myPair& a, myPair&b){
if (a.second < b.second) {
return true;
} else if (a.second == b.second) {
return a.first < b.first;
}
return false;
});
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push_back(v[i].first);
}
return result;
}
void printResult(vector<int>& result) {
cout << "[";
for (int a : result) {
cout << a << ",";
}
cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat{{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,0},
{1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1}};
auto result = kWeakestRows(mat, 3);
printResult(result);
mat = {{1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0}};
result = kWeakestRows(mat, 2);
printResult(result);
}
Output:
[2,0,3,]
[0,2,]
Complexity
- Runtime:
O(mn), wherem = mat.length, n = mat[i].length. - Extra space:
O(m).
Using C++ dictionary order
Standard C++ by default uses dictionary order to compare between such pairs of integers. You can switch the pair items to reduce some code.
Code 2
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int> kWeakestRows(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int k) {
using myPair = pair<int,int>;
vector<myPair> v;
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); i++) {
int num = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < mat[i].size(); j++) {
num += mat[i][j];
}
v.push_back(make_pair(num, i));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push_back(v[i].second);
}
return result;
}
void printResult(vector<int>& result) {
cout << "[";
for (int a : result) {
cout << a << ",";
}
cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat{{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,0},
{1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1}};
auto result = kWeakestRows(mat, 3);
printResult(result);
mat = {{1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0}};
result = kWeakestRows(mat, 2);
printResult(result);
}
Output:
[2,0,3,]
[0,2,]
Complexity
- Runtime:
O(mn), wherem = mat.length, n = mat[i].length. - Extra space:
O(m).
Solution 2: Searching and Sorting
You might notice the number of soldiers equals to the position of the first civilian. You do not need to compute the costly summation.
Code 1
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int> kWeakestRows(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int k) {
using myPair = pair<int,int>;
vector<myPair> v;
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); i++) {
int num = find(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), 0) - mat[i].begin();
v.push_back(make_pair(num, i));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push_back(v[i].second);
}
return result;
}
void printResult(vector<int>& result) {
cout << "[";
for (int a : result) {
cout << a << ",";
}
cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat{{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,0},
{1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1}};
auto result = kWeakestRows(mat, 3);
printResult(result);
mat = {{1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0}};
result = kWeakestRows(mat, 2);
printResult(result);
}
Output:
[2,0,3,]
[0,2,]
Complexity
- Runtime:
O(mn), wherem = mat.length, n = mat[i].length. - Extra space:
O(m).
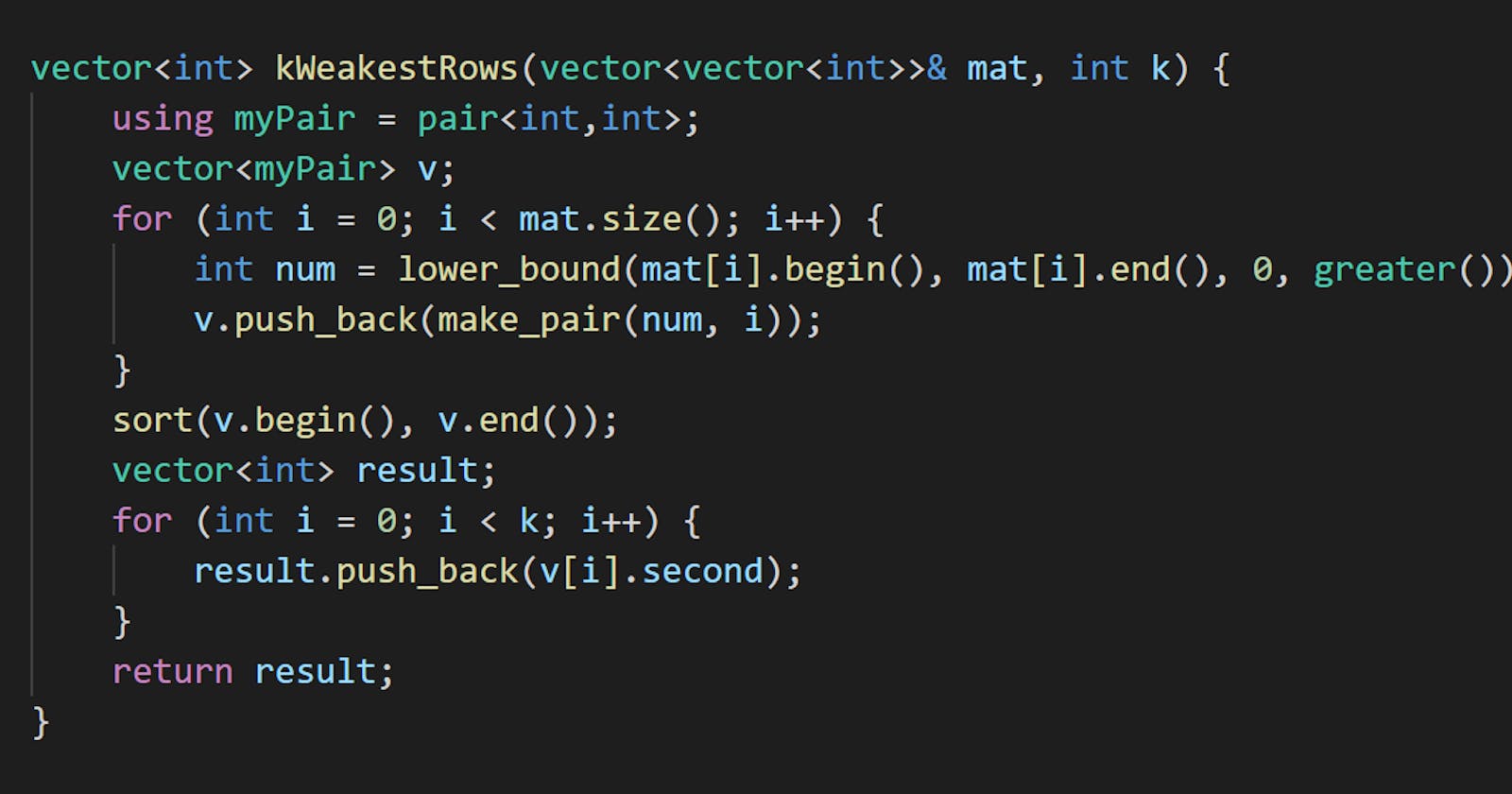
Binary search
The values in a row are sorted (first 1's then 0's). You can perform a binary search on it to reduce the runtime of the searching to O(logn) using std::lower_bound().
Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int> kWeakestRows(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int k) {
using myPair = pair<int,int>;
vector<myPair> v;
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); i++) {
int num = lower_bound(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), 0, greater()) - mat[i].begin();
v.push_back(make_pair(num, i));
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.push_back(v[i].second);
}
return result;
}
void printResult(vector<int>& result) {
cout << "[";
for (int a : result) {
cout << a << ",";
}
cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat{{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,0},
{1,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1}};
auto result = kWeakestRows(mat, 3);
printResult(result);
mat = {{1,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1},
{1,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0}};
result = kWeakestRows(mat, 2);
printResult(result);
}
Output:
[2,0,3,]
[0,2,]
Complexity
- Runtime:
O(mlogn), wherem = mat.length, n = mat[i].length. - Extra space:
O(m).