C++ Solution to Coding Challenge 1710. Maximum Units on a Truck
An example of the greedy algorithm
Problem statement
You are assigned to put some amount of boxes onto one truck. You are given a 2D array boxTypes, where boxTypes[i] = [numberOfBoxes_i, numberOfUnitsPerBox_i]:
numberOfBoxes_iis the number of boxes of typei.numberOfUnitsPerBox_iis the number of units in each box of the typei.
You are also given an integer truckSize, which is the maximum number of boxes that can be put on the truck. You can choose any boxes to put on the truck as long as the number of boxes does not exceed truckSize.
Return the maximum total number of units that can be put on the truck.
Example 1
Input: boxTypes = [[1,3],[2,2],[3,1]], truckSize = 4
Output: 8
Explanation: There are:
- 1 box of the first type that contains 3 units.
- 2 boxes of the second type that contain 2 units each.
- 3 boxes of the third type that contain 1 unit each.
You can take all the boxes of the first and second types, and one box of the third type.
The total number of units will be = (1 * 3) + (2 * 2) + (1 * 1) = 8.
Example 2
Input: boxTypes = [[5,10],[2,5],[4,7],[3,9]], truckSize = 10
Output: 91
Constraints
1 <= boxTypes.length <= 1000.1 <= numberOfBoxes_i, numberOfUnitsPerBox_i <= 1000.1 <= truckSize <= 10^6.
Solution: Greedy algorithm
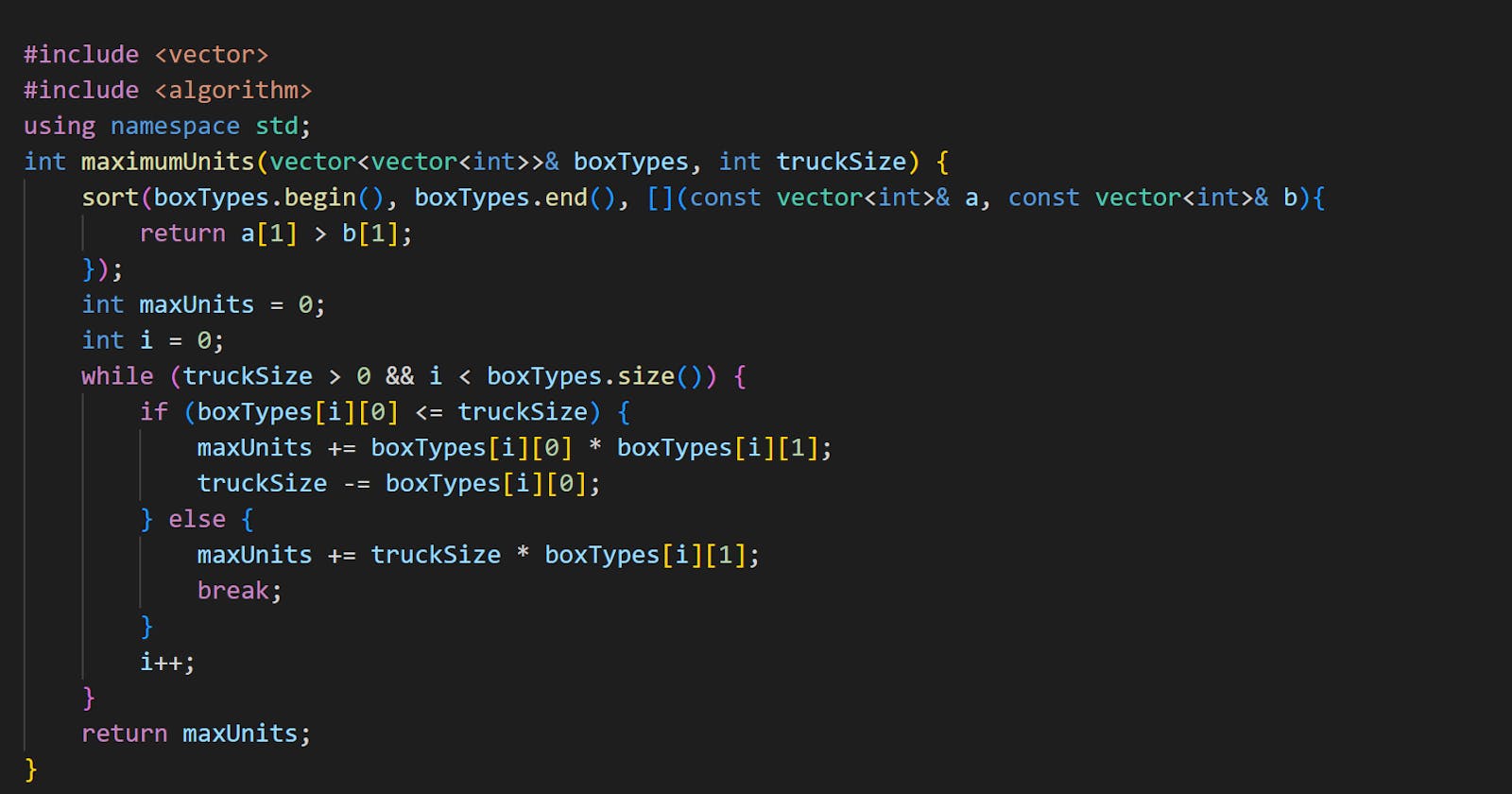
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int maximumUnits(vector<vector<int>>& boxTypes, int truckSize) {
sort(boxTypes.begin(), boxTypes.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){
return a[1] > b[1];
});
int maxUnits = 0;
int i = 0;
while (truckSize > 0 && i < boxTypes.size()) {
if (boxTypes[i][0] <= truckSize) {
maxUnits += boxTypes[i][0] * boxTypes[i][1];
truckSize -= boxTypes[i][0];
} else {
maxUnits += truckSize * boxTypes[i][1];
break;
}
i++;
}
return maxUnits;
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> boxTypes{{1,3},{2,2},{3,1}};
cout << maximumUnits(boxTypes, 4) << endl;
boxTypes = {{5,10},{2,5},{4,7},{3,9}};
cout << maximumUnits(boxTypes, 10) << endl;
}
Output:
8
91
Complexity
Runtime:
O(NlogN), whereN = boxTypes.length.Extra space:
O(1).