C++ Solution to Coding Challenge 1647. Minimum Deletions to Make Character Frequencies Unique
Problem statement
A string s is called good if there are no two different characters in s that have the same frequency.
Given a string s, return the minimum number of characters you need to delete to make s good.
The frequency of a character in a string is the number of times it appears in the string. For example, in the string "aab", the frequency of 'a' is 2, while the frequency of 'b' is 1.
Example 1
Input: s = "aab"
Output: 0
Explanation: s is already good.
Example 2
Input: s = "aaabbbcc"
Output: 2
Explanation: You can delete two 'b's resulting in the good string "aaabcc".
Another way is to delete one 'b' and one 'c' resulting in the good string "aaabbc".
Example 3
Input: s = "ceabaacb"
Output: 2
Explanation: You can delete both 'c's resulting in the good string "eabaab".
Note that we only care about characters that are still in the string at the end (i.e. frequency of 0 is ignored).
Constraints
1 <= s.length <= 10^5.scontains only lowercase English letters.
Solution: Delete the frequencies in sorted order
Your goal is to make all the frequencies be different.
One way of doing that is sorting the frequencies and performing the deletion.
Example 4
For s = "ceaacbb", the frequencies of the characters are: freq['a'] = 2, freq['b'] = 2, freq['c'] = 2 and freq['e'] = 1. They are already in sorted order.
Let the current frequency be the first frequency
freq['a'] = 2.The next frequency is
freq['b'] = 2, equal to the current frequency. Delete one appearance to make the current frequency be1.The next frequency is
freq['c'] = 2, bigger than the current frequency. Delete two appearances to make the current frequency to be0.Because the current frequency is
0, delete all appearances of the remaining frequencies, which isfreq['e'] = 1.In total there are
4deletions.
Code
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
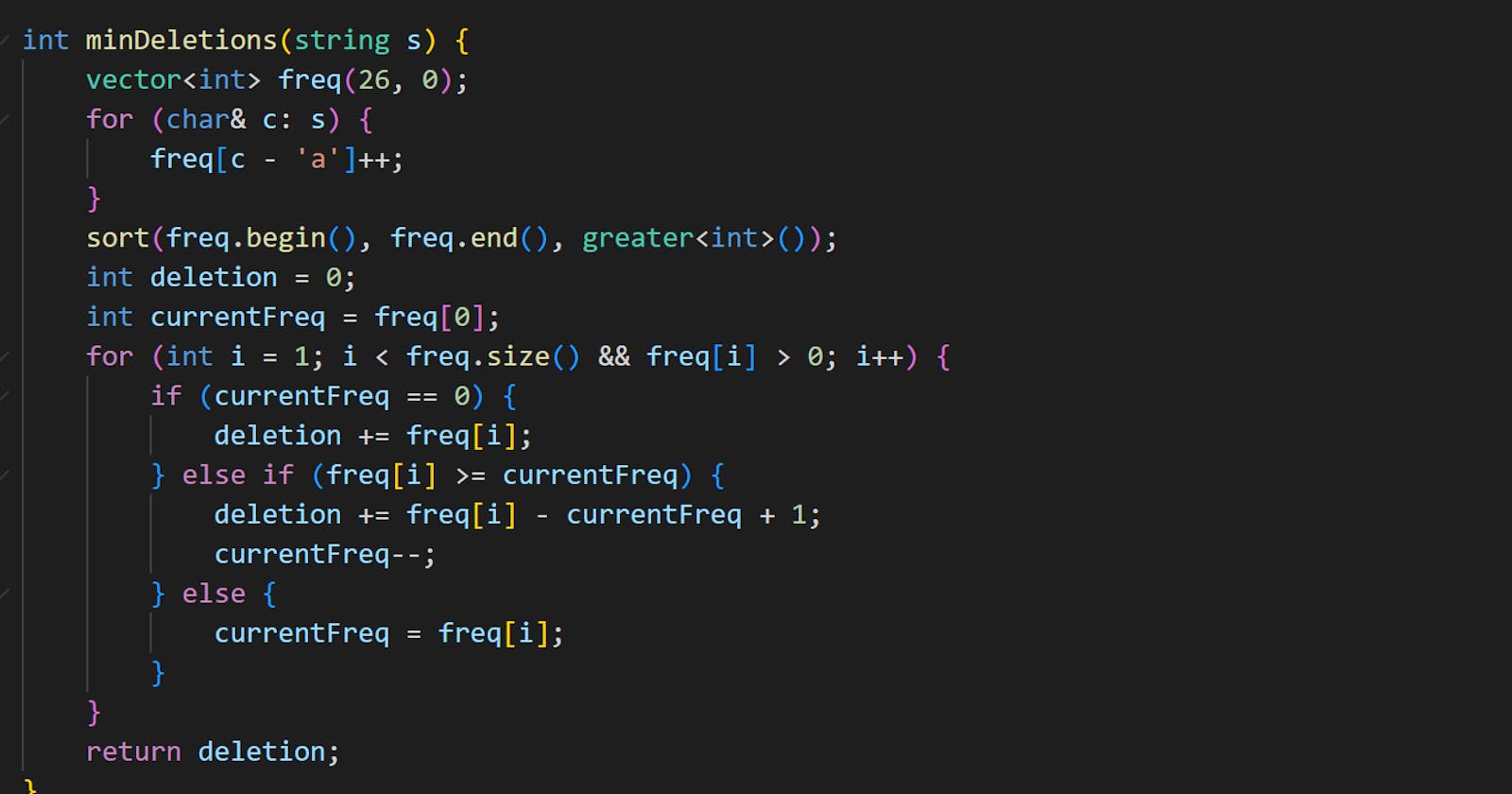
int minDeletions(string s) {
vector<int> freq(26, 0);
for (char& c: s) {
freq[c - 'a']++;
}
sort(freq.begin(), freq.end(), greater<int>());
int deletion = 0;
int currentFreq = freq[0];
for (int i = 1; i < freq.size() && freq[i] > 0; i++) {
if (currentFreq == 0) {
deletion += freq[i];
} else if (freq[i] >= currentFreq) {
deletion += freq[i] - currentFreq + 1;
currentFreq--;
} else {
currentFreq = freq[i];
}
}
return deletion;
}
int main() {
cout << minDeletions("aab") << endl;
cout << minDeletions("aaabbbcc") << endl;
cout << minDeletions("ceabaacb") << endl;
}
Output:
0
2
2
Complexity
Runtime:
O(N), whereN = s.length;Extra space:
O(1)since26is not a big number.