Problem statement
Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list. Return the linked list sorted as well.
Example 1

Input: head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]
Output: [1,2,5]
Example 2

Input: head = [1,1,1,2,3]
Output: [2,3]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 300]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100.- The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.
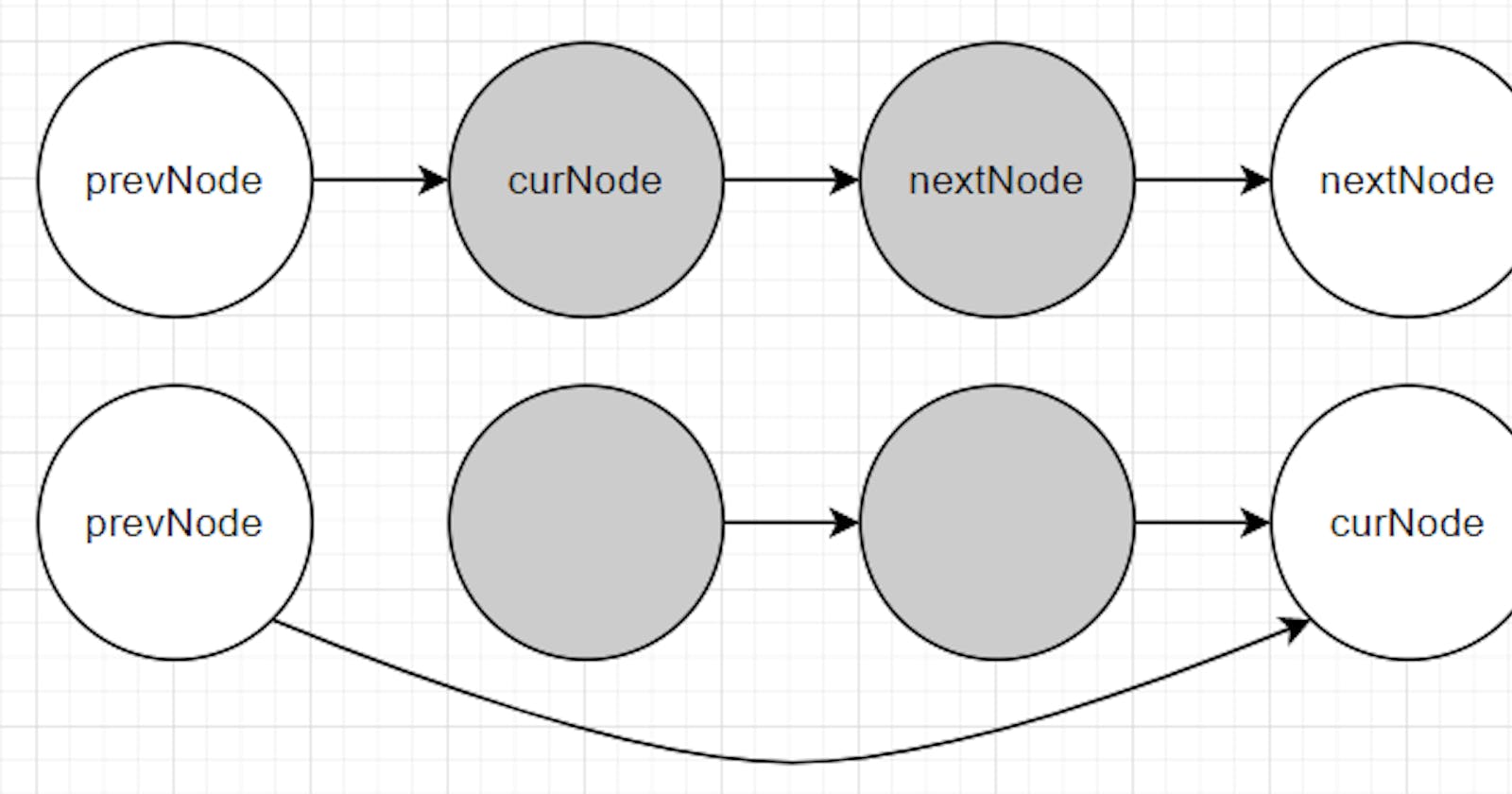
Solution: Drawing a picture of the removal
Case 1: There is no duplication on the current node (
nextNode.val != curNode.val).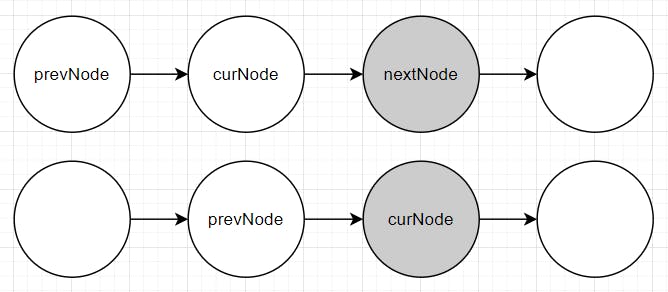
Case 2: A duplication happens (
nextNode.val == curNode.val).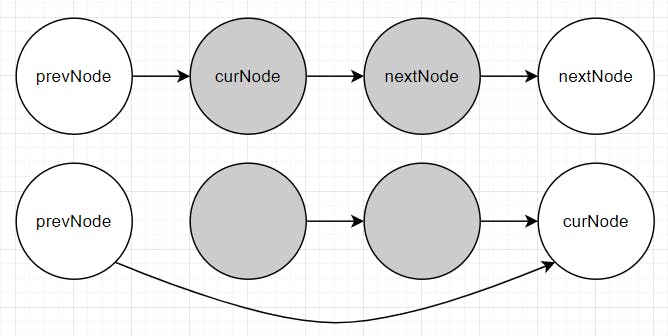
Code
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode prehead;
ListNode* prevNode = &prehead;
ListNode* curNode = head;
prevNode->next = curNode;
while (curNode) {
int val = curNode->val;
ListNode* nextNode = curNode->next;
int count = 0;
while (nextNode && nextNode->val == val) {
nextNode = nextNode->next;
count++;
}
if (count == 0) {
prevNode = curNode;
curNode = nextNode;
} else {
curNode = nextNode;
prevNode->next = curNode;
}
}
return prehead.next;
}
void printResult(ListNode* head) {
std::cout << "[";
while (head) {
std::cout << head->val << ",";
head = head->next;
}
std::cout << "]\n";
}
int main() {
{
ListNode five(5);
ListNode four2(4, &five);
ListNode four1(4, &four2);
ListNode three3(3, &four1);
ListNode three2(3, &three3);
ListNode three1(3, &three2);
ListNode two(2, &three1);
ListNode one(1, &two);
printResult(deleteDuplicates(&one));
}
{
ListNode three(3);
ListNode two(2, &three);
ListNode one3(1, &two);
ListNode one2(1, &one3);
ListNode one1(1, &one2);
printResult(deleteDuplicates(&one1));
}
}
Output:
[1,2,5,]
[2,3,]
Complexity:
- Runtime:
O(N), whereNis the length of the linked list. - Extra space:
O(1).
Implementation note
curNode = headis a corner case of any linked list problem because it has noprevNode. To avoid rewriting code for this special case, you could introduce a dummy node before thehead(here is theprehead).